API Developers Guide
Introduction
CommitCRM provides various tools in order to read/add/update information in the CommitCRM database. These tools include: Programming API and API by Email for updating the database, and an ODBC Link for pulling information from the database. The Commit API provides developers with a set of APIs which allow them to perform database transactions in order to add and update records in the CommitCRM database. The API can be used as a Programming API by embedding code which uses the API functions, or as an API by Email which allows you to send XML formatted emails which will be processed and executed.
- Programming API
The Commit API provides developers with a set of API functions which can be used in VB, C++, Delphi and any other programming language that lets you use a standard Windows dll file. It provides the ability to create a connection to CommitCRM's database, add new records to the database and update them.
- API by Email
The API by Email allows you to send XML formatted emails which contain database transactions. Commit Email Connector then pulls the incoming XML emails from your POP3 mail server, processes the email and performs the transactions in the XML transaction. XML formatted email gives you an API for the CommitCRM database, which allows you to perform many actions such as linking to external systems, receiving forms submitted from your web site, and more.
- ODBC Link
While the API provides the means for adding and updating information in the database, you should use ODBC Link in order to read information from the database. CommitCRM uses an open database structure and allows other applications to access the database using ODBC (Open Data Base Connectivity) for read-only purposes.
You can use ODBC Link in order to read data from the database and integrate it with an external system (i.e. Crystal reports, or any other application). You may also use the ODBC Link to read Database Record IDs and update existing records. This will be discussed later in this document.
Glossary
- Commit API (Application Programming Interface) - CommitCRM provides an API which allows you to add and update records in the CommitCRM database. The API includes a list of possible actions and parameters.
- ODBC Link (Open Data Base Connectivity) - ODBC is a function library which provides a common API for ODBC compliant databases. CommitCRM provides an open database and allows other applications to access the database using ODBC for read-only purposes.
- Record - Each entity in the CommitCRM database (such as Ticket, Account, Asset, Item, Appointment, Task, etc.) is considered a "record".
- Database fields - Each record contains a list of fields, each of which holds the record's data.
- Transaction – All additions or updates to record in the database are done by using a transaction. Each transaction includes the operation you wish to perform, the data type you wish to add/update and the additional parameters (database fields and their values).
- Transaction Parameters - Each transaction contains the parameters for performing the transaction: record type, list of database fields and a list of the values to be updated in these fields.
- External Application - This refers to the external program which integrates with CommitCRM in order to update the database. This name should be passed when performing updates to the database, and it will be saved in the CommitCRM record to indicate who performed the changes.
- Record ID (REC ID) - Each record in CommitCRM has a unique Record ID which is created when adding the record to the database. Every ID is 20 characters and should be transferred with the API transaction when you need to update an existing record.
Using Commit API
Commit API allows you to add and update records in the CommitCRM database, such as Accounts, Tickets, Assets, Items, Appointments, Tasks and more.
The updates are performed using transactions, where each transaction includes the operation you wish to perform, the data type you wish to add/update, and any additional parameters (i.e. record type, database fields and their values).
Every record added to the system is assigned a unique Record ID (REC ID) which is the database identifier for this record.
The Commit API allows you to perform the following operations.
- Add new records - if no Record ID is passed in the transaction, the API assumes that this is a new record, adds it to the system and creates a new Record ID for it.
- Update existing records - if the record ID is passed in the transaction, and the record exists, the system will update the record with the information in the transaction.
In both cases, the system will try to set default values for fields which do not exist in the incoming transaction. If it fails, the action will fail with an error.
Note that in order to read data from the CommitCRM database, you should use the ODBC Link, which provides a read-only link for the CommitCRM database. See more details in Retrieving data using ODBC.
Workflow
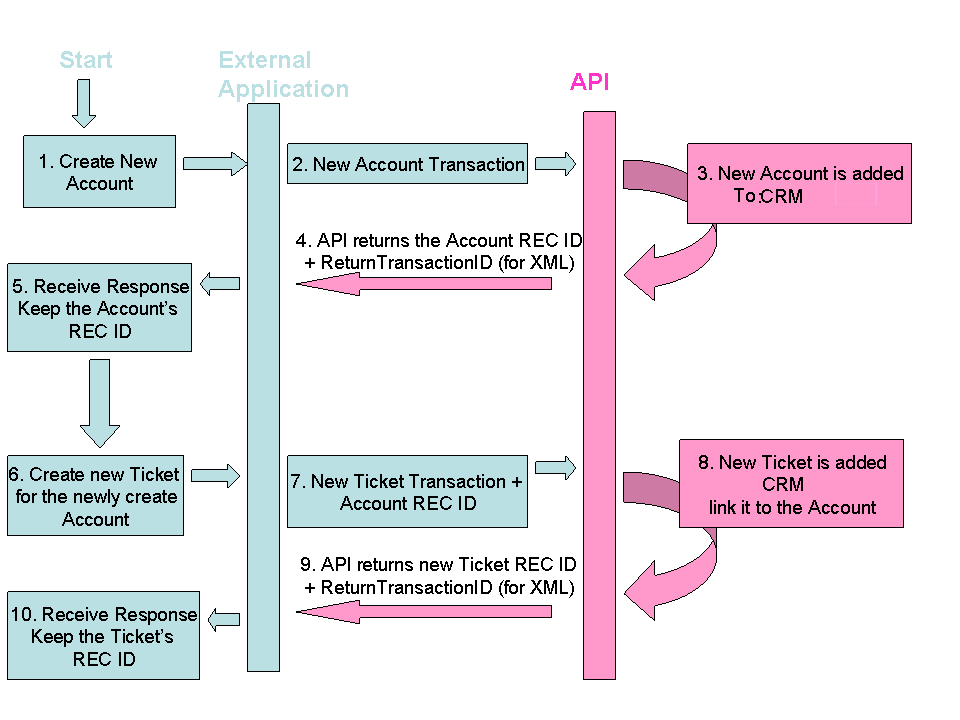
Following is a sample work-flow, which demonstrates the process of adding a new Account, and then adding a new Ticket to this Account, using the Commit API.
Note that the API can return two parameters to the External Application:
- The Commit REC ID - when adding new records to the database, this will contains the new record ID.
- The ExternalTransactionID (relevant for XML transaction only) - In case the external application passes a parameter to be returned with the response, the ExternalTransactionID will be returned as-is to in the response.
The External Application should keep the REC ID which is returned from the API response. This allows you to later update the existing records with new data or add records related to it (such as opening a Ticket under the Account).
Updating existing records
In order to update an already existing record in the database (e.g. add a Ticket to an Account, update an Account's phone number, add a new Charge to an existing Ticket, etc.), you should pass the record's unique identifier to the API so it will update the existing record rather than create a new Account. The record's unique identifier is referred to as the Record ID (REC ID).
The Record ID can be obtained in the following ways:
- API Response (as in the flow above) - You can extract the newly created Record ID from the Email Response when adding new records with the API. This requires the developer to process the API responses, and extract the returning REC ID for each newly added record.
- ODBC Link - Use the ODBC Link to find relevant records (Accounts, Tickets, etc.), and read all information from the database, including the unique Record ID.
- Manually - from the Account's Notes tab, at the bottom, right-click the REC ID field and copy it.
Once you have obtained the Record ID you can pass the Record ID as a parameter for the API and update this record.
Programming API
The Programming API allows you access the CommitCRM database and perform transactions from within a program (using various programming language). This means you can embed code which accesses the CommitCRM database from within your own application, and add your own functionality which updates the database.
The programming API executes database transactions. Each transaction uses API methods provides by the API dll file which is located in the CommitCRM installation. Both the Programming API and the API by Email use the same dll for performing the transactions.
Note that the API provides the tools needed for adding/updating information in the database. In order to retrieve data, you should use the ODBC link which allows you to connect to the database and retrieve data directly from the tables. You can read more about it in the ODBC Data Retrieval section.
You can find more information and samples in the API Code Samples section.
API by Email (XML transaction)
The API by Email operates under the Commit Email Connector module, which automatically processes incoming emails arriving at a defined public email address. The Email may contain XML formatted messages which contain API transactions, and provides a full API to CommitCRM.
The Email Connector pulls incoming emails from your POP3 mail server, and processes the email. When an email containing XML formatted message is detected, the system analyzes the XML content of the email and performs the transactions written in the XML. You may set the Email Connector to send automatic replies in response to XML formatted email.
The API by Email executes database transactions. Each transaction uses API methods provided by the API dll file which is located in the CommitCRM installation. Both the Programming API and the API by Email use the same dll for performing the transactions.
Note that the API provides the tools for adding/updating information in the database. In
order to retrieve data, you should use the ODBC link which allows you to connect to the
database and retrieve data directly from the tables. You can read more about it in the
ODBC Data Retrieval section.
You can find more information and samples in XML samples.
ODBC Data Retrieval
CommitCRM uses an open database and allows other applications to access it using ODBC (Open Data Base Connectivity) for read-only purposes. While the API provides the means for adding and updating information in the database, it is preferred to use ODBC to read information from the database.
You can use ODBC Link to read data from the database and integrate it with an external system (i.e. Crystal reports, or any other application). You may also use the ODBC Link in order to read the Database Record ID and update existing records (see Updating existing records).
Activation Notes:
- The ODBC drivers are well tested and work well, however, please note that the Commit Support team doesn't provide "pure ODBC" support.
- NEVER use ODBC to modify or delete data; use it for READ purposes only. Modifying data should be done using the Commit API.
- The ODBC Link can be used with your installed version of CommitCRM, and only requires installing an external driver. Before working with the API we recommend that you backup the database.
Below are the database table names and their meaning:
| CommitCRM Record | Database Table Name |
|---|---|
| Accounts | Cards |
| Tickets | Tickets |
| Charges | Slips |
| Assets | Assets |
| Appointments | Events |
| Tasks | Events |
| History Notes | NoteBook |
| Opportunities | Opps |
| Documents | Docs |
| Knowledge Base | KBArticles |
For the database fields list, please refer to API Reference Manual section. You can find detailed instructions for using the ODBC Link in the Installing ODBC Driver section.
Installing ODBC Driver
Product Overview
The Advantage ODBC Driver is an ODBC version 3 driver based on the Advantage Client Engine that provides SQL access to the Advantage Database Server. The driver provides
full support for the "Minimum" ODBC SQL grammar specification, as well as many functions
included in the "Core" and "Extended" grammar specifications. When used with the
Advantage Database Server, ODBC users can have the
application stability, performance and reduced network traffic benefits of client/server
architecture.
Installation on Windows
Like other ODBC drivers, the Advantage ODBC Driver is installed and managed using the
ODBC Administrator Utility. This utility works with the ODBC Driver Manager to configure
ODBC data sources. At runtime, the ODBC Driver Manager works with available drivers and
their configured data sources. If you have previously installed ODBC drivers, the ODBC Administrator may already be installed on your workstation. The icon for the Administrator is usually found in the Control Panel.
To install the Advantage ODBC Driver:
- Click here to download the Advantage ODBC setup program.
- Run the Setup program.
- Proceed through the setup windows to complete installation.
Data Source Setup for Windows
Once the Advantage ODBC Driver is installed, a data source needs to be configured to use
the Advantage ODBC Driver. The data source is an entry in the Windows Registry. When a
data source is defined for the Advantage Driver, all information specific to the Advantage
Driver and database files is stored under the Data Source entry in the Windows 95/98/ME/
NT/2000/2003/XP Registry.
The database files and indexes must be stored on your file server, and the Advantage
Database Server must be loaded in order to access the files.
The Data Source settings may be modified at any time. Using the ODBC Administrator, you may modify the Data Source and Option settings. For specific information about the screen fields see the Data Source Setup Screen.
To Setup the Data Source:
- From the ODBC Administrator, click Add.
- Highlight the Advantage SQL ODBC line, and click OK.
- Type a unique data source name. For example, type AdvData. This name is used by applications to reference the data source.
- Specify the database or data dictionary path. Type a valid path name to a mapped drive on the server where the Advantage Database Server is installed or the path and file name of your Advantage Data Dictionary. Click Browse to select a database path or check the Data Dictionary check box and then browse to select a data dictionary file. Note Multiple Advantage data sources may need to be defined for your environment. If different settings are needed for ODBC connections in one application, separate data sources may be required.
- Review the options and change them to your desired setup.
- Once the Options are reviewed and/or altered, click OK to exit and save the settings. The new data source is displayed.
- Click Close to exit the ODBC Administrator.
ODBC Data Source Entries for Windows
In Microsoft Windows, the entries are registry settings found on HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\ODBC\ODBC.INI\ (your unique data source name) or HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\ODBC\ODBC.INI (your unique data source name). Unless specified otherwise, all registry entries can be setup by the Advantage ODBC Driver setup utility. See Data Source Setup for Windows and Data Source Setup Screen for more information. ODBC Data Source Keys.
ODBC Data Source Keys
The following ODBC registry is required for the driver to load:
| Registry Entry | Comments |
|---|---|
| DataDirectory=data path | 'data path' should be a valid path name for files locations (e.g., x:\data). This path is used to automatically select all tables in the specified directory. |
| DefaultType=Advantage | Sets a certain type of database files to use Advantageproprietary ADT/ADI/ADM files. |
| ServerTypes=3 | Allows the Driver to use the remote or local server |
The following ODBC registry keys are optional:
| Registry Entry | Comments |
|---|---|
| AdvantageLocking=ON \ OFF | The default is ON to use the Advantage proprietary locking. |
| CharSet=OEM \ ANSI | The default character collation setting is ANSI. If OEM is specified, Language must be indicated as well. |
| Language=USA | Used if CharSet=OEM. |
| Description=String | This is provided for easier administration. |
| Locking=RECORD \ FILE | Indicates whether updates lock the entire file or the individual records that are updated. The default is RECORD. |
| MaxTableCloseCache=n | N is the number of tables to hold in cache when cursors are opened and closed. The default is 25. |
| MemoBlockSize=n | N is the size of the Advantage memo blocks in tables that are created by the ODBC driver. The default value is 8 for Advantage proprietary table (ADT/ADM). |
| Rows=TRUE \ FALSE | Select whether deleted rows are displayed. If True, deleted rows are displayed. The default is False. |
| TrimTrailingSpaces=TRUE \ FALSE | The default is False. If True is specified, trailing spaces in character fields will be removed prior to returning the values to the application. |
Troubleshooting ODBC in 64 Bit Operating Systems
The Commit ODBC drivers are mainly distributed for 32-bit operating systems; however, the same drivers are supported on the 64-bit operating systems (I.e. Windows 7 x64), and can be used to retrieve data from the CommitCRM database.
Configuring Data Source in 64-Bit Systems
When installing the ODBC drivers on 64-bit operating systems, the ODBC drivers may not be displayed in the default ODBC manager in windows control panel. In order to view the 32-bit ODBC manager in a 64-bit operating system, you’ll need to browse to %windir%\SysWOW64\odbcad32.exe and run the 32 bit ODBC Administrator manually. Once the data source has been configured there, you should be able to select the data source in your 3rd party ODBC programs.
Samples
The Commit API allows you to add/update the following entities:
- Accounts
- Assets
- Tickets
- Charges
- Appointments
- Tasks
- History Notes
- Opportunities
- Documents
- Knowledge Base Articles
Each API method requires a list of parameters which contain the field names and their values. The field names are the Database field names. You can see each field's name within the application (so you can verify which field you are about to update), by right-clicking the field and selecting Field Settings > Advanced Tab > view the Tech. Rec ID field.
You can view the complete list of database fields in the API Reference Manual above.
Following are samples for using the API by Email and the Programming API. The samples are basic and provide an easy starting point.
See API Code Samples.
API Reference Manual
The API allows you to add/update the following entities:
- Accounts
- Assets
- Tickets
- Charges (and Contract-price Charges)
- Appointments
- Tasks
- History Notes
- Opportunities
- Documents
- Knowledge Base Articles
You can find a detailed listing of the database fields in the API Reference Manual.